I’m sure most of you have heard about AI. And there’s a good chance you’ve come across the Internet of Things (IoT) at some point.
But what happens when these two revolutionary technologies join forces?
You get the Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT). And it’s changing the world we know today, from your home to entire industries.
Quick Answer: What is AIoT?
AIoT = IoT devices + Artificial Intelligence + Real-Time Autonomous Decision-Making
It’s a network of connected devices that use AI to learn, analyze data and make intelligent decisions without human intervention.
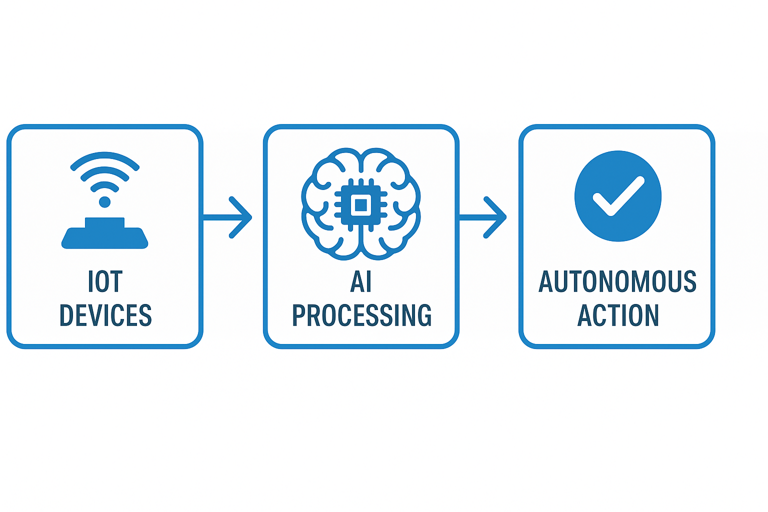
Imagine you’re pulling into your driveway after a long day. Before you reach the door, your home has already adjusted the temperature to something cosy, turned on your favorite evening playlist and started brewing a cup of your usual tea. That’s AIoT quietly working in the background of modern life.
These aren’t just smart devices that follow pre-programmed rules. They’re connected devices that also learn from your behavior, adapt to your preferences and make decisions in real-time. Your voice assistant that seems to understand you better each week? That’s AIoT. That fitness tracker offering surprisingly personalized insights? AIoT again.
Understanding AIoT Basics
If you’re thinking, “Alright, but what does that actually mean?”, here’s the answer.
AI (Artificial Intelligence) refers to systems that can learn, reason and make decisions in ways that mimic human intelligence. IoT (Internet of Things) describes the network of physical devices connected via the Internet, constantly collecting and sharing data.
When these technologies come together, you get AIoT.
How AIoT Actually Works
The AIoT process follows a pretty straightforward path.
- Sensors embedded in connected devices collect real world data like temperature, motion, sound or biometric information
- This data is transmitted to processing systems, either cloud based platforms or local edge computing devices
- AI algorithms analyze the incoming data streams, identifying patterns, making predictions and triggering automated responses
The result is a self improving system that gets smarter over time. Don’t worry, though – we’re talking about helpful thermostats, not Skynet.
Why AIoT Represents a Paradigm Shift
Traditional IoT devices are essentially data collectors. They measure and report, but humans must interpret the information and take action. AIoT changes this dynamic completely by combining IoT’s continuous data flow with AI’s decision making capabilities.
Consider two scenarios. A standard IoT security camera records footage for later review – you react after something happens. An AIoT security system identifies suspicious activity in real-time, alerts you instantly and secures doors. One is reactive, the other proactive.
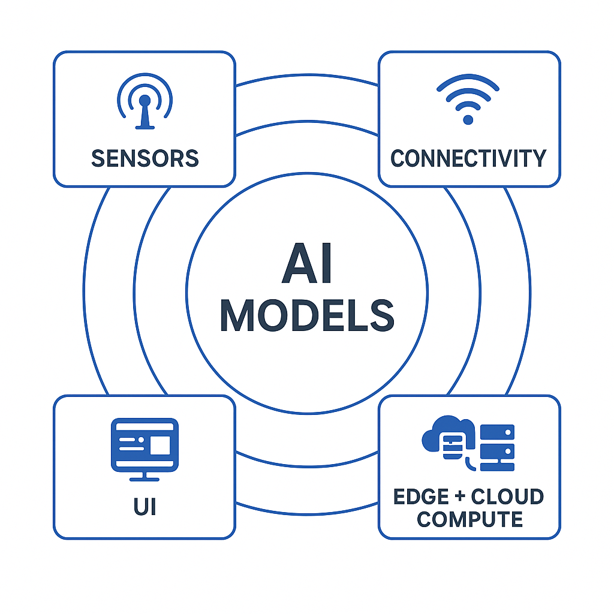
The Main Components of AIoT Architecture
An AIoT ecosystem is built from several interconnected components, each serving a critical function.
Sensors: The Eyes and Ears
Sensors serve as the data collection tools for any AIoT deployment.
They capture real world information including temperature, humidity, motion, light, sound and biological signals like heart rate or blood oxygen levels. A sophisticated AIoT setup typically employs multiple sensor types, creating a well rounded view of the environment.
Common sensor types include:
- Temperature sensors that track climate conditions continuously
- Proximity and motion sensors that detect movement and presence
- Biometric sensors that read fingerprints, facial features or vital signs
- Pressure sensors that monitor fluid or air pressure in industrial and medical applications
- Environmental sensors that measure air quality, humidity or light levels
Connectivity: The Nervous System
The most sophisticated sensors imaginable are useless if they can’t transmit data effectively.
AIoT systems rely on various connectivity technologies, each suited to specific requirements. Options include Bluetooth for short range, low power connections, Wi-Fi for high bandwidth local networks, 5G for fast, wide area connectivity, and specialized protocols like LoRaWAN or NB-IoT for long range, battery powered connected devices.
The choice depends on your specific needs. How far data does data need to travel? How much battery life matters? Do large volumes of data need transmitting? Are quick responses required?
Data Processing and Storage Infrastructure
Once collected, data needs both processing and storage.
Large scale AIoT implementations typically rely on cloud computing platforms where remote servers handle the heavy processing work. However, there’s a growing trend toward edge computing, where data is processed close to its source rather than sent to distant servers on the Internet.
Edge AI offers huge advantages for time sensitive applications. When a self-driving car needs to brake immediately, there’s no time to send data to a cloud server and wait for a response. Processing needs to happen locally, at the edge, enabling split second decisions that can be life saving in time critical scenarios.
The two approaches serve different purposes:
- Cloud based processing works well when you need massive computational power and can tolerate slight delays
- Edge processing is essential for immediate responses, particularly in scenarios where safety is paramount
Many modern AIoT systems use a hybrid approach, processing urgent decisions at the edge while sending data to the cloud for deeper analysis and long term learning.
AI Algorithms: The Brain
This is where the true magic happens.
Sophisticated AI algorithms analyze data streams, recognize patterns, make predictions and trigger actions. The more they learn, the smarter they become.
For example, an AI model might distinguish between a person, a pet and a car entering a driveway, triggering different responses for each scenario. Perhaps a doorbell notification for a person, a simple log entry for your pet or an alert if an unfamiliar vehicle approaches.
User Interface: The Control Panel
For all this intelligence to be useful, people need ways to interact with AIoT systems.
Modern interfaces range from smartphone apps and web dashboards to voice commands and augmented reality (AR) displays. The best interfaces feel intuitive, putting powerful capabilities in your hands without overwhelming complexity.
AIoT Applications In The Home and Across Industries
The real power of AIoT becomes clear when you see it in action.
Smart Homes and Connected Buildings
Your alarm goes off and before you’re fully awake, your coffee maker has already started brewing. The smart mirror in your bathroom displays your calendar while you brush your teeth. Your car warms up in the garage because the system knows you leave at 7:15 AM. You haven’t pressed a single button, yet everything’s ready exactly when you need it.
Smart thermostats like Nest or Ecobee learn your temperature preferences and daily routines, automatically adjusting settings to maximize comfort while minimizing energy costs. Lighting systems adapt based on natural light levels and occupancy. Security systems can recognize familiar faces and can distinguish between the mailman and a potential intruder.
In commercial buildings, AIoT goes even further with predictive maintenance systems that detect equipment problems before failures occur, saving money and preventing disruptions.
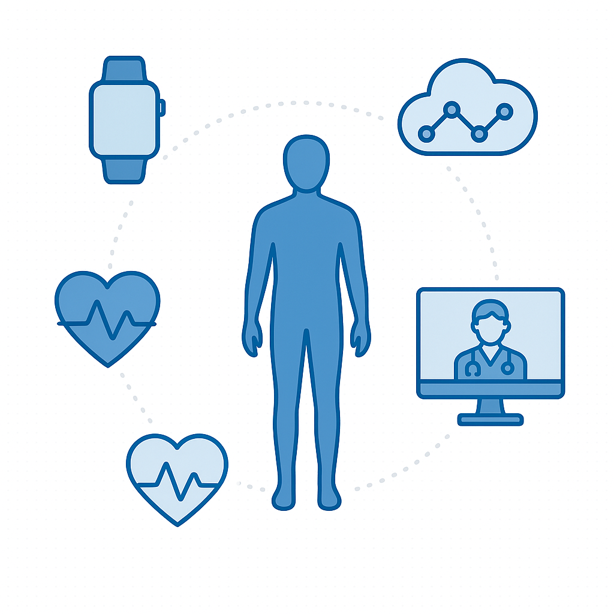
Healthcare and Medical AIoT Applications
Healthcare represents one of AIoT’s most promising frontiers.
Wearable devices now track not just steps but heart rate, blood oxygen, sleep patterns and stress levels. AI algorithms analyze this continuous stream of health data, detecting concerning patterns and alerting both patients and healthcare providers about potential issues.
In hospitals, AIoT enables remote patient monitoring, allowing medical staff to oversee multiple patients at the same time. Smart pill dispensers ensure medication is taken on schedule, while predictive models help doctors anticipate complications before they become serious.
Industrial Manufacturing and Smart Industry
Factories equipped with AIoT systems operate with unprecedented efficiency.
Sensors monitor equipment health, predicting maintenance needs before breakdowns occur. AI powered quality control systems inspect products at speeds impossible for human workers, identifying defects with remarkable accuracy.
Collaborative robots (cobots) work safely alongside humans, with AIoT systems ensuring real-time safety checks and seamless coordination. These smart factories can adjust production schedules dynamically based on demand forecasts, equipment availability and supply chain conditions.
Transportation and Logistics
Transportation is another sector being revolutionized by AIoT.
Fleet management systems track vehicle locations, monitor driver behavior, predict maintenance needs and optimize routes based on traffic conditions. Autonomous vehicles represent the ultimate AIoT application. They process enormous amounts of sensor data every second to navigate safely.
In logistics, AIoT optimizes warehouse operations, from inventory management to robotic picking systems.
Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring
Smart agriculture uses AIoT to maximize yields while minimizing resource consumption.
Soil sensors monitor moisture levels, nutrient content and pH balance. Weather stations and satellite data feed into AI models that optimize irrigation schedules. Drones equipped with multispectral cameras identify crop health issues invisible to the human eye.
Retail and Customer Experience
Retailers leverage AIoT to improve customer experiences and streamline operations.
Smart shelves detect inventory levels and automatically trigger restocking orders. Computer vision systems analyze foot traffic patterns, helping optimize store layouts.
In Amazon Go stores, sensors and AI virtually eliminate checkout lines. Customers simply take items and leave. Their accounts are charged automatically.
Addressing Security and Implementation Challenges
While AIoT offers tremendous potential, security, privacy and its implementation should be carefully considered.
Security and Privacy
AIoT devices collect continuous streams of personal data, such as voice patterns, health metrics, location information and behavioral patterns. Without proper safeguards, this data faces potential misuse. Organizations must prioritize encryption, adopt a zero-trust security model, and ensure regular security updates and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. The interconnected nature of AIoT systems also creates potential vulnerabilities, making strong cybersecurity practices especially important.
Implementation Realities
Deploying AIoT at scale requires significant upfront investment in sensors, networking infrastructure and processing platforms. Perhaps more challenging is the skills gap. Organizations need experts in data science, IoT engineering and cybersecurity. As AIoT systems make increasingly autonomous decisions, questions around accountability and regulatory compliance become more pressing, especially in sectors like healthcare and finance.
Despite these challenges, the trajectory is clear. AIoT adoption continues growing as technology costs decline and best practices evolve.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of AIoT
AIoT continues to expand, driven by advances in AI algorithms, cheaper sensors, faster networks and innovative applications. A few trends are particularly worth keeping an eye on.
Next-Generation Connectivity: 6G
While 5G is being actively rolled out in today’s AIoT applications, 6G research is already underway, promising near-instantaneous wireless communication and support for massively dense device networks. These advanced networks will enable AIoT deployments we can barely imagine today.
Hyper-Personalization
Future AIoT systems will deliver unprecedented personalization, moving far beyond today’s basic recommendations.
Healthcare treatment plans tailored to individual genetics, lifestyle and real-time biometrics. Educational systems that adapt dynamically to each student’s learning patterns. Vehicles that automatically adjust not just to who’s driving, but to their current stress levels and cognitive state.
This personalization goes beyond convenience and has the potential to improve outcomes across healthcare, education and quality of life.
The Age of Intelligent Things
We’ve entered an era where everyday objects can perceive, learn and respond. AIoT is quietly shaping our homes, workplaces and cities right now.
Intelligence is moving into the world around us. Not replacing people, but augmenting how we already live and work. Yes, there are real considerations around privacy, security and trust, but with thoughtful adoption, the benefits far outweigh the risks.
Welcome to the age of intelligent things. Your future self will thank you for paying attention. And who knows? Your smart home might beat you to it.