Most houseplants die slowly while we guess whether they need more light or less water. You stick your finger in soil that feels bone dry on top, water generously, then discover it was soaking wet an inch below the surface. Smart plant monitors eliminate this guesswork by measuring exact soil conditions and sending data straight to your phone.
These compact sensors measure soil moisture, light intensity and temperature, and some models also estimate nutrient levels, transforming plant care from trial-and-error into data driven precision. If you’ve ever killed a plant despite “doing everything right”, you’ll immediately understand the value of knowing what’s actually happening at root level.

What Smart Plant Monitors Do
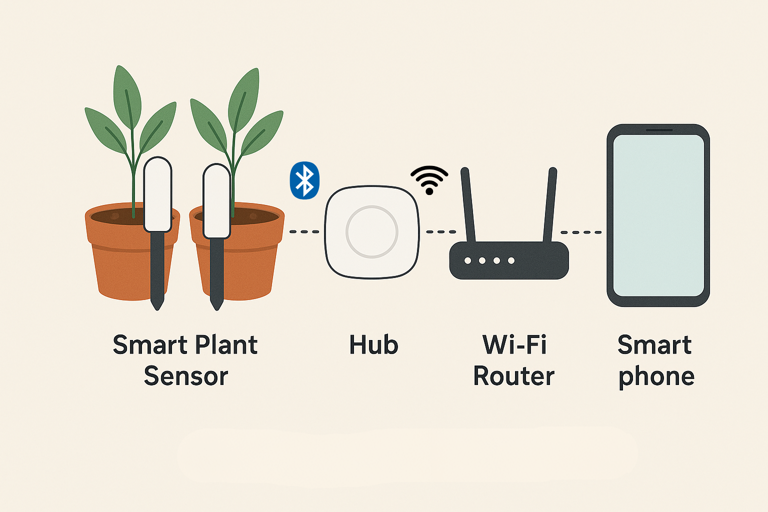
Smart plant monitors are small electronic devices that continuously track environmental conditions affecting plant health. You insert them into soil near your plant’s roots, where they measure moisture, temperature, light exposure and sometimes nutrient content.
These sensors transmit data wirelessly to your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. The companion app translates raw measurements into actionable insights, telling you when to water, whether to move your plant closer to a window or if the temperature is too cold for optimal growth.
Unlike traditional moisture meters that provide a single reading, smart sensors build a complete picture of your plant’s environment over days and months. You’ll start spotting patterns, like how your pothos drinks twice as much water in summer, or how your “bright” corner only gets medium light in winter.
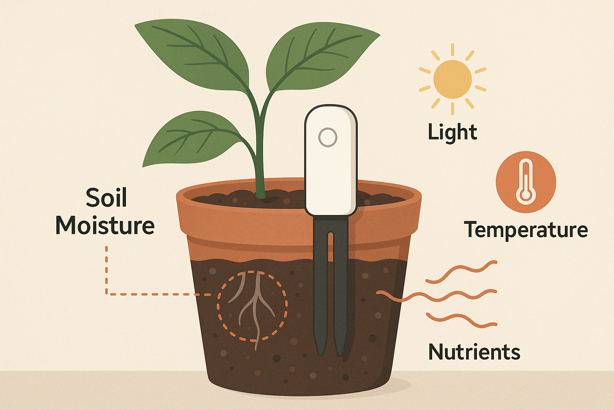
How Smart Plant Sensors Work
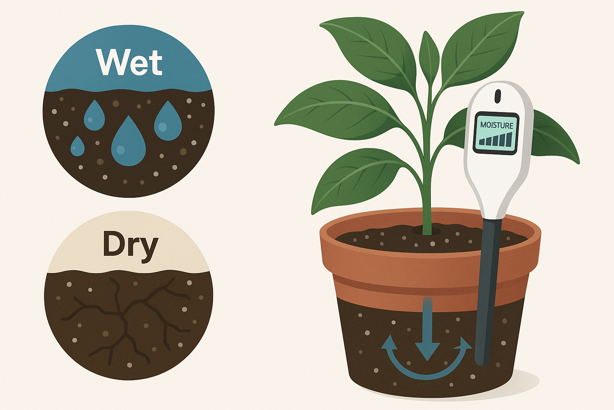
Soil Moisture Detection
Most consumer sensors report relative moisture values (0–100% scales), not true volumetric percentages that professional agricultural sensors measure. That’s fine for houseplants, as you don’t need lab grade precision to know when your snake plant is thirsty.
The accuracy of readings from entry level resistive (EC-based) sensors often varies by 10-20%, depending on soil type, salinity and compaction. Higher end capacitance sensors tend to be more consistent across common potting mixes and can achieve around 3-5% accuracy in ideal lab or calibration conditions, though real world performance still depends on placement and soil composition.
Light Measurement
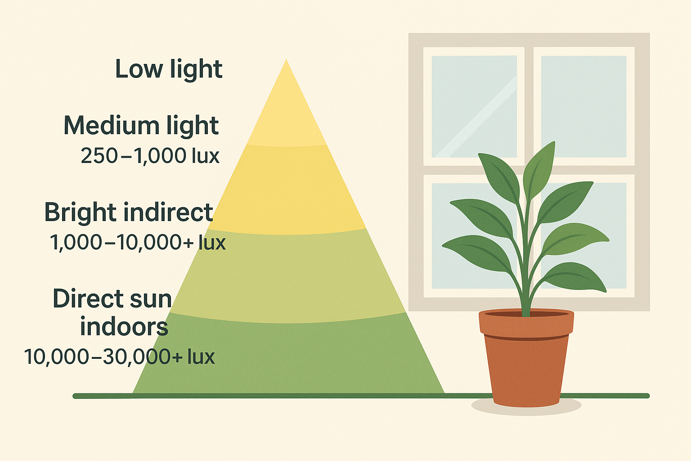
Built-in sensors measure illuminance (or light intensity) in lux, helping you place plants correctly.
- Low light: Less than 250 lux (north-facing window, far from windows)
- Medium light: 250-1,000 lux (east-facing window, filtered light)
- Bright indirect: 1,000-10,000+ lux (south-facing with sheer curtain)
- Direct sun indoors: 10,000-30,000+ lux (unobstructed south window)
Some sensors struggle to accurately interpret LED grow lights, though tracking patterns over time still helps optimize placement. The issue is that sensors measure brightness visible to humans (lux), not the specific light wavelengths plants use for photosynthesis (PAR/PPFD).
Temperature and Nutrients
Temperature sensors track ambient conditions, helping you identify cold drafts or hot spots near radiators. Most houseplants prefer 65-75°F for optimal growth.
Advanced sensors measure soil conductivity to estimate fertility. Important limitation: Electrical conductivity (EC) cannot distinguish between useful nutrients and unwanted salt build-up, providing general guidance rather than precise nutrient analysis. For detailed nutrient information, traditional soil testing remains more accurate.

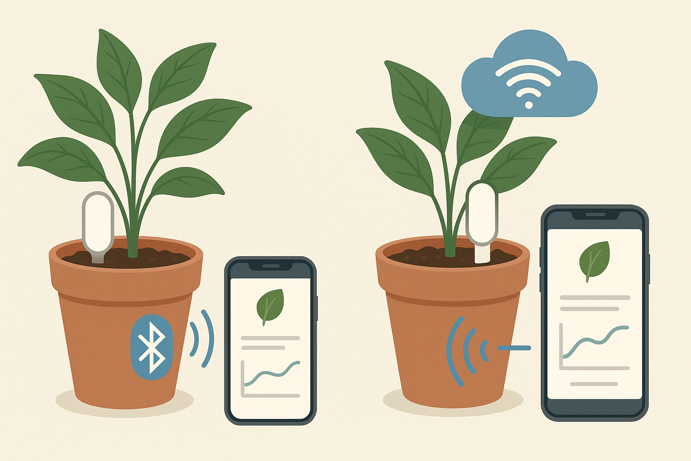
Wireless Connectivity
Bluetooth sensors work within 10-30 feet indoors (walls dramatically reduce range). Wi-Fi models allow remote monitoring from anywhere with Internet access. Sensors continuously collect data and either store it locally or transmit to the cloud, with your app processing information and alerting you when action is needed.

What to Look For When Choosing a Sensor
Accuracy and Reliability
Standard EC-based sensors typically offer 10-20% accuracy, adequate for general houseplant care. Premium capacitance sensors may achieve around 3-5% accuracy in ideal conditions, making them a worthwhile investment for expensive orchids or rare plants, but overkill for most collections.
Connectivity Options
Bluetooth works fine if you’re regularly near your plants. Wi-Fi becomes valuable for frequent travelers or plants in rarely visited rooms. Check whether apps require constant connection or instead sync periodically with stored data.
Battery Life and Power
Bluetooth sensors run on CR2032 coin cells lasting 6-12 months. Many Wi-Fi sensors use either rechargeable batteries (often charged via USB-C) or replaceable AA/AAA cells, and they usually need recharging or new batteries every 1-4 months, depending on update frequency and signal strength.
App Quality
Essential app features include large plant databases (3,000-6,000+ species), custom care recommendations, historical graphs, push notifications and multi-plant management. Test the interface before committing. Some apps require subscriptions for advanced features.
Before buying, read recent app store reviews for connectivity issues, apps not updated in over a year or subscription fees. A poorly designed app undermines the entire value of a smart sensor.
Price and Value
Smart plant sensors range from $12 for basic Bluetooth models to $60+ for advanced Wi-Fi versions. Consider initial cost, hub requirements, subscription fees, battery replacement and how many plants you’ll monitor. Mid-range sensors ($25-40) offer the best balance for most home growers.
Types of Smart Plant Sensors
Bluetooth Sensors
The most common and affordable option, transmitting data when your phone is nearby (10-30 feet indoors).
Pros: Lower cost ($15-35), long battery life (6-12 months), no hub required, works without Internet
Cons: Requires proximity to sync, limited range through walls, no remote notifications, may need manual syncing
Best for: Indoor enthusiasts who check plants regularly and want affordable entry into smart monitoring
Wi-Fi Sensors
Connect directly to your home network for remote monitoring from anywhere ($30-60 per sensor with rechargeable batteries).
Pros: Check plants from anywhere, real-time push notifications, continuous cloud logging, smart home integration
Cons: Higher cost, requires Wi-Fi coverage, battery life 1-4 months between charges, Internet dependent
Best for: Frequent travelers, office plants, anyone wanting remote monitoring
Hub Based Systems
Central hubs connect multiple Bluetooth sensors to your home network, bridging short range Bluetooth with remote access.
Pros: More affordable sensors than Wi-Fi models, remote access via hub, monitors many plants simultaneously, additional smart home features
Cons: Hub cost ($20-50), requires electrical outlet, another device to maintain, hub must be within Bluetooth range
Best for: Users monitoring 5+ plants who want remote access without Wi-Fi per-sensor costs
Quick Comparison
- Bluetooth: Best budget option for houseplant beginners ($15-35, simple setup)
- Wi-Fi: Best for travelers (anywhere access, auto-alerts)
- Hub-based: Best for large collections of 10+ plants (affordable scaling)
Setting Up Your Sensor
Setup usually takes less than 10 minutes.
- Download the companion app (iOS/Android)
- Install batteries or charge the device
- Insert sensor 2-4 inches deep near root zone, angled to avoid damage
- Pair via Bluetooth or connect to Wi-Fi following app prompts
- Select your plant species from database or create custom profile
- Set notification preferences and data logging frequency
- Calibrate if needed (some sensors require dry/saturated soil calibration)
Place probes away from pot edges where moisture differs from the root zone. For pots over 10 inches, consider multiple sensors or weekly rotation.
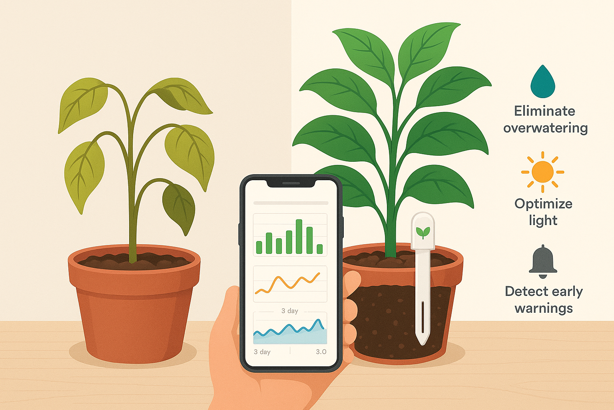
Practical Benefits of Smart Plant Sensors
Eliminate guesswork: Know exactly when soil moisture drops below optimal levels, preventing overwatering and underwatering, the most common houseplant killers.
Learn plant patterns: See how quickly different plants use water across seasons, how light changes throughout the year and how environmental shifts impact growth.
Prevent problems early: Detect moisture stress, temperature extremes or nutrient depletion before visible symptoms appear.
Optimize placement: Light sensors reveal your “bright” living room might only provide medium light, or that north facing windows give adequate indirect light for certain species.
Travel confidently: Remote monitoring through Wi-Fi sensors means checking plants while away, with alerts telling friends exactly when to water.
Grow demanding plants: Orchids, carnivorous plants or tropical species with precise requirements become manageable with continuous monitoring.
Save resources: Water only when needed based on real data, avoiding wasted water and fertilizer from arbitrary schedules.

Limitations to Know About
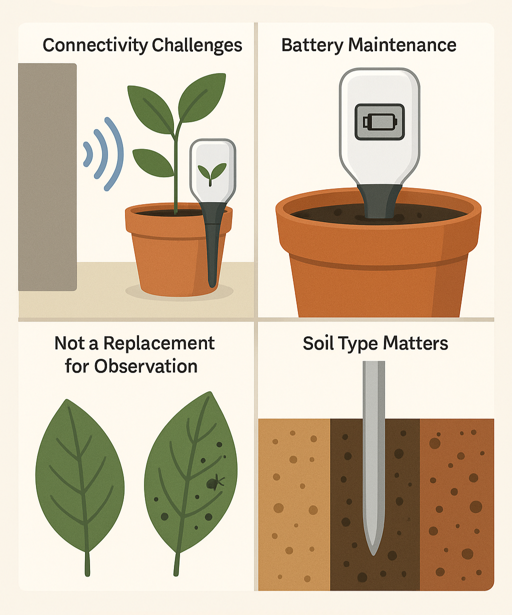
Connectivity Challenges
Bluetooth range struggles through walls and floors. Wi-Fi sensors solve this but require stable network coverage. Some users report issues switching between multiple sensors rapidly.
Battery Maintenance
Real world battery life varies based on transmission frequency and conditions. Wi-Fi recharging is easy to forget until low battery alerts appear.
Not a Replacement for Observation
Sensors measure specific metrics but can’t detect pests, diseases or mechanical damage. Use them as tools complementing, not replacing, visual inspection.
Soil Type Matters
Heavy clay, peat based mixes and chunky orchid bark affect sensor accuracy differently. Most sensors are calibrated for standard potting soil and may give inconsistent readings with these alternatives, so focus on trends over time rather than absolute numbers.
Smart Sensors vs. Traditional Moisture Meters
Traditional analog meters cost $5-15 and provide instant readings with no batteries required. However, they only show current conditions, so no historical data, alerts or tracking. You must remember to check them regularly and readings vary with soil type.
Smart sensors cost more initially but offer continuous monitoring, data trends and automatic alerts. For serious enthusiasts managing multiple plants, this ongoing insight justifies the higher price. Casual owners with a few hardy plants might find traditional meters sufficient.
Smart Home Integration
Many sensors work with Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, Apple HomeKit and IFTTT for voice commands and automation. Advanced users can create custom routines like automatically logging data to spreadsheets or triggering smart irrigation, though most find standalone apps sufficient.

Which Plant Sensor Is Best for You?
- Beginners: Start with 2-3 affordable Bluetooth sensors on your most valuable plants
- Plant collectors: Hub based systems for monitoring 10+ plants
- Frequent travelers: Wi-Fi sensors with push notifications
- Rare/expensive plants: Premium sensors with advanced metrics like VPD (in systems that include humidity sensors)
- Outdoor containers: Weather resistant sensors with solar charging
Getting the Most from Your Sensor
Calibrate your understanding: Spend 2-3 weeks observing how your plant responds to sensor readings. Your pothos might thrive at 35% moisture while the app suggests 40-50%.
Track seasonal changes: Plant water needs vary dramatically between winter and summer. Review historical data to spot patterns and adjust care routines.
Use sensors strategically: Rotate one sensor between similar plants weekly or place permanent sensors only on high value specimens.
Clean probes regularly: Wipe monthly with a damp cloth or use diluted vinegar (as per manufacturer instructions) for mineral build-up, which can affect accuracy.
Replace batteries proactively: Don’t wait for warnings. Replace on a schedule (twice yearly) to avoid data gaps.
Sensor-ble Plant Care
Tired of playing plant detective? Smart plant monitors turn “maybe it needs water” into “soil moisture at 23% – water now”. They measure what your eyes can’t see and alert you before damage occurs. No sensor replaces observation, but the combination of technology and attention creates better outcomes than either alone.
Your plants have been telling you what they need all along. Now you can finally hear them.
Looking for alternatives to standalone sensors? Smart plant pots integrate monitoring directly into containers for streamlined care, while smart gardens eliminate monitoring entirely with automated hydroponic systems that grow fresh herbs year-round.