This post may contain affiliate links. If you click through and make a purchase, we may earn a commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support our work and allows us to continue providing valuable content. For more information, please see our disclosure policy.

You’ve arrived home after a long day and your house welcomes you like a well trained butler. The lights brighten to your preferred evening setting, your thermostat adjusts to the perfect temperature and your favorite playlist starts playing softly in the background. This is the reality of smart home technology in 2025.
If you’ve been curious about changing your house into a smart home but felt overwhelmed by all the options and technical jargon, you’re not alone. The smart home industry can seem complex, but getting started is actually much simpler than you might think.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about creating your first smart home setup, from understanding the basics to choosing devices and creating those impressive automations that’ll make everyday life much more convenient.
What Makes a Home “Smart”?
A smart home connects your everyday devices to the Internet, allowing them to communicate with each other and respond to your commands.
Your smart home ecosystem centers around smart speakers or displays (Amazon Echo, Google Nest Hub, Apple HomePod, for example), smartphone apps for remote control and voice assistants for hands free commands.
Smart home devices communicate through several protocols. Here are a few popular examples:
- Wi-Fi: The same network powering your laptop and phone, ideal for bandwidth intensive devices.
- Bluetooth: Perfect for close range connections like smart locks and speakers.
- Zigbee and Z-Wave: Specialized mesh protocols that relay signals between devices for extended range.
Assessing Your Smart Home Potential
Before making your first purchase, take a strategic look at your current living situation and daily routines. This assessment will help you prioritize which smart devices will bring you the most value.
Consider Your Living Space
- Renters: Focus on portable devices that don’t require permanent installation.
- Homeowners: Can explore built-in solutions like smart switches and hardwired systems.
- Large homes: May need mesh Wi-Fi systems and devices with extended range.
- Apartments: Might benefit from compact, multi-purpose devices.
Identify Your Pain Points
- Constantly adjusting the thermostat? A smart thermostat could save energy and effort.
- Frequently leaving lights on? Smart lighting with scheduling is your solution.
- Worried about home security? Smart cameras and doorbells provide valuable peace of mind.
- Always losing keys? Smart locks eliminate the need for physical keys entirely.
Budget Planning: Smart home setups can range from $100 for basic starter kits to thousands for comprehensive systems. Start with one or two highly useful devices and expand gradually.
Choosing Your Smart Home Ecosystem
One of the most important decisions you’ll make is selecting a primary smart home platform. This choice affects device compatibility, app management and long term expandability.
We’ve broken this decision down in a dedicated comparison of the best smart home hubs, including which options make the most sense for first time smart home setups.
Amazon Alexa
Best for: Frequent online shoppers and users who want the widest device compatibility
Strengths:
- Largest selection of compatible third-party devices.
- Excellent voice recognition and natural language processing.
- Strong integration with Amazon services.
- Extensive automation capabilities through Routines.
Considerations:
- Privacy concerns due to Amazon’s data collection practices.
- Can feel overwhelming due to sheer number of features.
Google Home/Nest
Best for: Android users and Google service enthusiasts
Strengths:
- Superior search capabilities and contextual understanding.
- Seamless integration with Google services (Calendar, Gmail, Maps).
- Excellent smart display options with visual responses.
- Strong AI-powered suggestions and learning.
Considerations:
- Fewer third-party integrations compared to Alexa.
- Limited offline functionality.
Apple HomeKit
Best for: iPhone/iPad users prioritizing privacy and security
Strengths:
- Industry leading privacy and security features.
- Seamless integration with iOS devices and Siri.
- Local processing reduces reliance on cloud services.
- Premium build quality for certified devices.
Considerations:
- Smaller selection of compatible devices.
- Generally higher prices for HomeKit certified products.
- Limited voice assistant capabilities compared to competitors.
Pro Tip: While it’s best to choose one primary ecosystem, many devices work across multiple platforms. You can always integrate devices from different ecosystems later using universal protocols like Matter.
Best Smart Home Devices for Beginners
Start your smart home journey with these high impact devices that offer immediate benefits and serve as building blocks for more advanced setups.
Smart Speakers or Displays
These serve as the command center for voice control and device coordination.
Top Picks:
- Amazon Echo Dot: Affordable entry point with solid sound quality.
- Google Nest Hub: Combines voice control with visual interface.
- Apple HomePod Mini: Premium option for Apple ecosystem users.

Smart Lighting
Transform your home’s ambiance while saving energy with programmable lighting.
Options:
- Smart Bulbs: Easy to install, work in existing fixtures (Philips Hue, LIFX).
- Smart Switches: Control multiple bulbs, require basic electrical work.
- Smart Dimmers: Adjust brightness and create mood lighting.
Benefits:
- Schedule lights to turn on/off automatically.
- Adjust color and brightness remotely.
- Create different lighting scenes for various activities.
- Significant energy savings with LED technology.

Smart Thermostats
Optimize comfort while reducing energy bills through intelligent climate control.
Popular Models:
- Google Nest Thermostat: Learning algorithms and sleek design.
- Ecobee SmartThermostat: Room sensors for better temperature distribution.
- Honeywell T9: Affordable option with geofencing capabilities.
Key Features to Look For:
- Learning capabilities that adapt to your schedule.
- Geofencing that adjusts temperature based on your location.
- Energy usage reports and optimization suggestions.
- Integration with your preferred smart home ecosystem.

Smart Plugs and Outlets
Turn any regular appliance into a smart device instantly.
Use Cases:
- Coffee makers that start brewing on schedule.
- Lamps controlled by voice or app.
- Space heaters with automatic shut-off timers.
- Holiday decorations with automated schedules.

Smart Security Devices
Strengthen your home security with connected cameras, doorbells and sensors.
Essential Security Devices:
- Video Doorbells: See and speak to visitors remotely (Ring, Nest Doorbell).
- Indoor Cameras: Monitor pets or check on home while away.
- Motion Sensors: Trigger lights or alerts when movement is detected.
- Smart Locks: Keyless entry with temporary access codes for guests.

Setting Up Your Smart Home Network
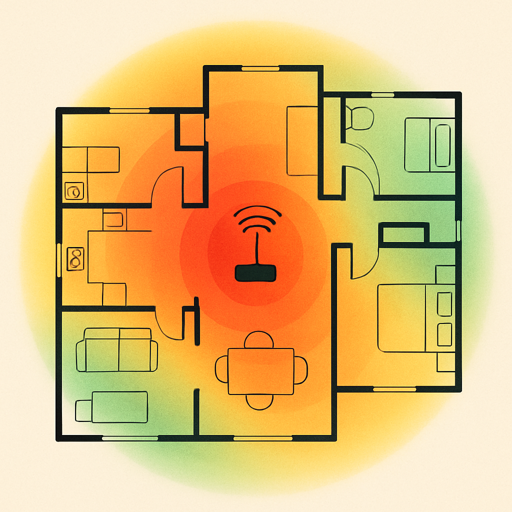
Your smart home is only as reliable as the network supporting it. A stable Wi-Fi setup keeps your devices running smoothly.
Wi-Fi Network Optimization
Coverage Assessment: Walk through your home with a Wi-Fi analyzer app to identify dead zones and weak signal areas. Pay special attention to:
- Basements and upper floors.
- Rooms far from your main router.
- Areas with thick walls or multiple floors between devices and router.
Network Solutions
- Single Router: Adequate for small homes or apartments up to 1,500 sq ft.
- Mesh Wi-Fi System: Ideal for larger homes or complex layouts (eero, Google Nest Wifi, ASUS AiMesh).
- Wi-Fi Extenders: A budget friendly option for targeting specific dead zones.
Network Security Best Practices
Protect your smart home with these essential security measures.
- Strong Authentication: Use unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA).
- WPA3 Encryption: Ensure your router uses the latest supported security protocol. If WPA3 is not available, WPA2/WPA3 mixed-mode or WPA2-only are reasonable alternatives.
- Network Segmentation: Keep smart devices on a separate guest network.
- Automatic Updates: Enable firmware updates for all devices.
- Device Monitoring: Regularly review connected devices and remove unused ones.
Device Placement Strategy
Router Positioning
- Central location in your home.
- Elevated position (shelf or wall mount).
- Away from interference sources (microwaves, cordless phones, baby monitors).
- Adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
Smart Device Considerations
- Hub devices (like smart home controllers) should be centrally located.
- Battery powered devices benefit from strong Wi-Fi signals to conserve power.
- Consider physical obstructions when planning device locations.
Installing and Configuring Smart Devices
Most modern smart devices are designed for easy self-installation, but following best practices ensures a more hassle-free setup and optimal performance.
Pre-Installation Checklist
Before unboxing your new smart device:
- Verify Compatibility: Ensure the device works with your chosen ecosystem.
- Check Network Requirements: Confirm your Wi-Fi supports the device’s needs.
- Download Required Apps: Install manufacturer apps and ecosystem apps.
- Prepare Network Information: Have your Wi-Fi name and password ready.
- Plan Device Location: Consider signal strength and functionality needs.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Physical Setup
- Follow manufacturer instructions for mounting or placement.
- Ensure adequate power supply and test basic functionality.
Network Connection
- Open the manufacturer’s app and follow guided setup.
- Connect device to your Wi-Fi network.
- Allow initial software updates to complete.
Ecosystem Integration
- Add device to your smart home platform (Alexa, Google, HomeKit).
- Test voice commands and app controls.
- Configure desired automations or schedules.
Creating Automations and Routines
This is where your smart home truly becomes intelligent, responding to your needs without constant manual input.
Understanding Automation Types
Time Based Automations
- Lights that turn on at sunset and off at bedtime.
- Thermostat adjustments that align with your daily schedule.
- Coffee maker that starts brewing every weekday morning.
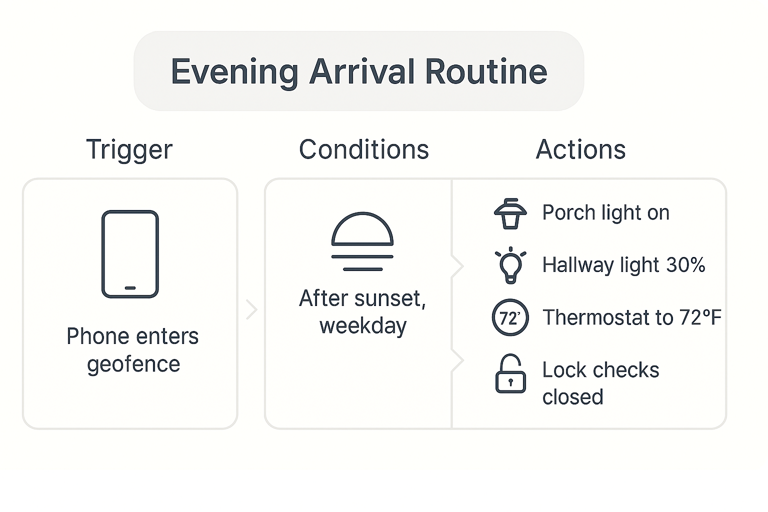
Trigger Based Automations
- Motion sensors that activate security lighting.
- Door sensors that trigger welcome routines when you arrive home.
- Weather based adjustments to heating and cooling systems.
Location Based Automations
- Geofencing that adjusts settings when you leave or approach home.
- Vacation mode that randomly turns lights on and off for security.
- Energy saving modes that activate when everyone leaves the house.
Example Automation Templates
Morning Routine
- Gradual light brightening 30 minutes before alarm.
- Smart thermostat increases temperature.
- Coffee maker begins brewing.
- Morning news briefing plays on smart speaker.
- Bathroom fan turns on automatically.
Evening Routine
- Outdoor lights turn on at sunset.
- Indoor lights dim to relaxing levels.
- Thermostat adjusts to sleep temperature.
- Security system arms automatically.
- White noise machine activates in bedroom.
Away Mode
- All non-essential devices turn off.
- Security cameras activate recording.
- Random light patterns simulate occupancy.
- Thermostat enters energy saving mode.
- Smart locks double check security status.
Advanced Automation Techniques
Conditional Logic: Create more sophisticated automations using “if this, then that” logic. For instance:
- “If motion detected AND it’s after dark AND security system is disarmed, THEN turn on pathway lights”.
- “If weather forecast shows rain AND it’s a weekday morning, THEN send reminder to take umbrella”.
Multi-Device Sequences: Chain multiple device actions together:
- Movie night: Dim lights → Close smart blinds → Turn on TV → Set thermostat to comfortable temperature → Start popcorn maker.
Smart Home Security Essentials
As you connect more devices, protecting both your network and privacy becomes critical.
Authentication and Access Control
Account Security
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all smart home accounts.
- Use a password manager for unique, complex credentials.
- Regularly audit and remove unused access permissions.
- Review what data your devices collect and how it’s used.
Network Protection
- Segment smart devices on a separate network when possible.
- Disable remote access features you don’t actively use.
- Monitor for unusual device behavior or unknown connections.
Physical Security Considerations
Camera Best Practices
- Avoid pointing cameras toward bedrooms and bathrooms.
- Inform household members about camera locations.
- Enable privacy modes that disable recording when you’re home.
- Use activity logs to monitor for unauthorized access.
Smart Lock Safety
- Maintain backup access methods (physical key or keypad).
- Audit access codes regularly and remove old ones.
- Ensure locks have backup power or manual override options.

Expanding Your Smart Home System
Once you’ve mastered the basics, numerous opportunities exist to improve your smart home setup with specialized devices and advanced integrations.
Advanced Device Categories
Kitchen and Appliances
- Smart refrigerators with inventory tracking and meal planning.
- Connected ovens with remote preheating and cooking monitoring.
- Smart dishwashers that optimize cycles based on load sensors.
- Voice controlled garbage disposals and faucets.
Health and Wellness
- Air quality monitors that trigger air purifiers.
- Smart sleep tracking with automatic environment adjustments.
- Connected fitness equipment with progress tracking.
- UV sanitizing devices with smart scheduling.
Energy Management
- Solar panel monitoring and optimization systems.
- Smart water heaters with usage pattern learning.
- Electric vehicle chargers with grid integration.
- Whole home energy monitoring with usage insights.
Outdoor and Garden
- Smart irrigation systems with weather integration.
- Pool automation with temperature and chemical monitoring.
- Outdoor security lighting with motion and schedule controls.
- Smart mailbox sensors with delivery notifications.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Even the most reliable smart home systems occasionally need attention. Developing good maintenance habits prevents most issues and keeps your system chugging along nicely.
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Monthly
- Install app and firmware updates
- Check battery levels and replace as needed.
- Test critical automations.
Quarterly
- Adjust schedules for seasonal changes.
- Audit user access and permissions.
- Back up automation configurations.
Annually
- Evaluate system for upgrades.
- Update all passwords.
- Assess network performance needs.
Common Issues and Solutions
Connectivity Problems: Devices frequently offline or slow response times.
- Check Wi-Fi signal strength and restart router.
- Update device firmware.
- Consider mesh network upgrade for better coverage.
Automation Failures: Scheduled actions not triggering or incomplete execution.
- Review automation logic for errors.
- Verify all devices are online and responsive.
- Simplify complex routines into smaller steps.
Voice Recognition Issues: Smart speakers not responding or misunderstanding commands.
- Re-train voice models in app settings.
- Reduce background noise sources.
- Adjust wake word sensitivity.
Battery Drain: Frequent replacements or devices going offline unexpectedly.
- Improve device placement for better signal strength.
- Reduce polling frequencies in device settings.
- Consider hardwired alternatives for high usage devices.
When to Seek Professional Help
Some smart home challenges benefit from professional assistance.
- Electrical Work: Installing smart switches, outlets or hardwired devices.
- Network Infrastructure: Comprehensive Wi-Fi system design and installation.
- Security System Integration: Connecting professional monitoring with smart devices.
- Complex Troubleshooting: Persistent connectivity or performance issues.
The Future of Your Smart Home
So what’s next in the exciting realm of the smart home?
Emerging Technologies
Matter Protocol: This new industry standard promises to eliminate compatibility issues between different smart home ecosystems, allowing devices from different manufacturers to work together effortlessly.
AI and Machine Learning: Future smart homes will become increasingly predictive, learning your preferences and anticipating your needs without explicit programming.
Energy Integration: Smart homes are becoming central to residential energy management, with integration between solar panels, battery storage, electric vehicles and grid services.
Your Smart Home Journey Starts Now
Creating a smart home doesn’t happen overnight and it certainly doesn’t need to break the bank. The key is to start with devices that solve real problems in your daily life, then gradually expand as you discover new opportunities for automation and convenience.
Whether you start with a simple smart plug and a voice assistant or dive in with a comprehensive security and automation system, you’re taking the first step toward a more connected, efficient and comfortable living space.
Welcome to the future of living – one smart decision at a time.

